China is the manufacturing superpower | Hacker News. This statement, while seemingly bold, reflects a reality shaped by decades of strategic planning, economic reforms, and a massive workforce. We’ll explore China’s journey to manufacturing dominance, examining its key sectors, competitive advantages, and the global implications of its unparalleled production capacity. We’ll also delve into the challenges and uncertainties that lie ahead, painting a picture of both the triumphs and potential pitfalls of this economic powerhouse.
From its humble beginnings to its current position as a global manufacturing giant, China’s ascent is a fascinating case study in economic development. We’ll look at the specific government policies that fueled this growth, the role of technology and innovation, and how China’s cost structure compares to other manufacturing hubs. Understanding China’s manufacturing prowess is crucial for anyone navigating the complexities of global trade and supply chains.
China’s Manufacturing Dominance: China Is The Manufacturing Superpower | Hacker News

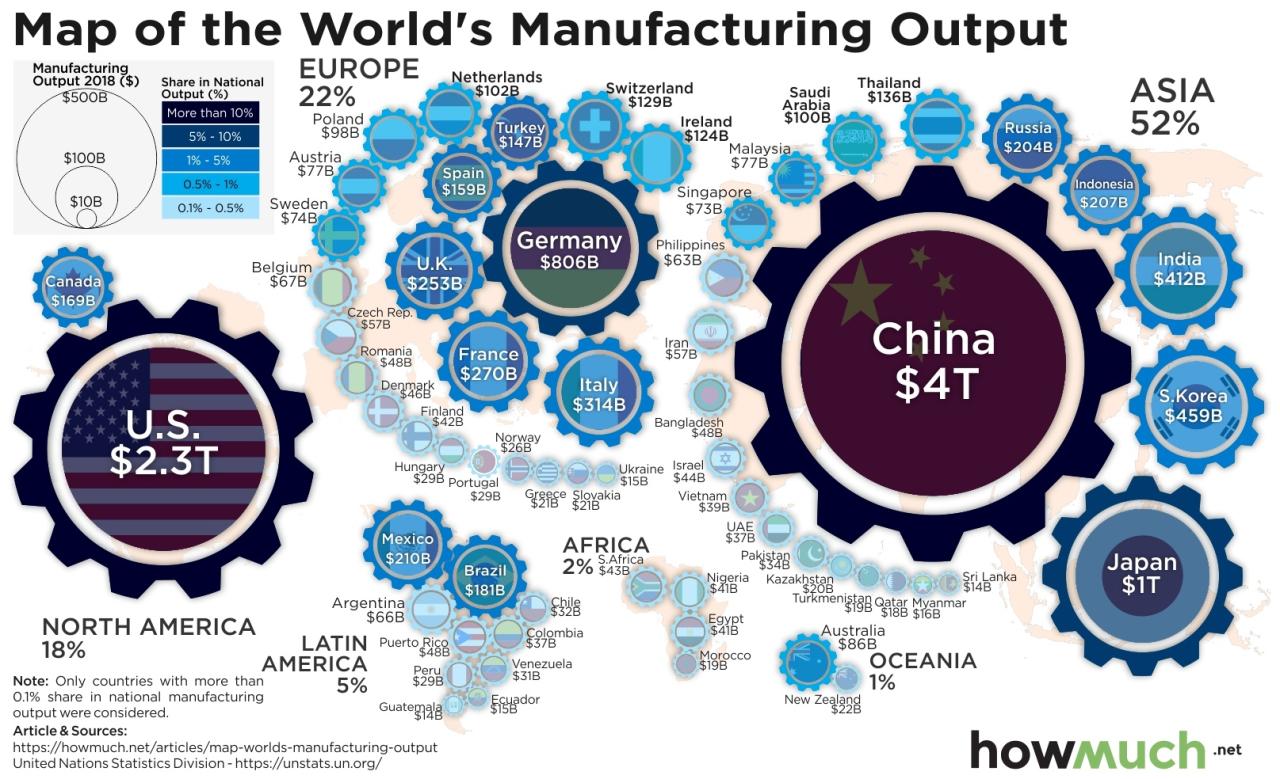
China’s rise as the world’s manufacturing powerhouse is a remarkable story of economic transformation, driven by strategic government policies, a vast and adaptable workforce, and a relentless focus on export-oriented growth. This dominance, however, is not without its challenges and potential vulnerabilities. This article explores the historical context of China’s manufacturing ascent, its key sectors and competitive advantages, its role in global supply chains, and the challenges and future outlook for its continued leadership.
China’s Manufacturing Dominance: Historical Context
China’s journey to manufacturing dominance is a multi-decade process marked by significant policy shifts and economic reforms. From a largely agrarian economy, it transitioned into a global manufacturing hub, surpassing other nations in production volume and export value. This transformation involved a deliberate strategy of attracting foreign investment, developing infrastructure, and fostering export-oriented industries.
| Date | Event | Impact | Supporting Evidence |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1978 | Economic Reforms initiated by Deng Xiaoping | Opened China to foreign investment and market-oriented reforms, laying the foundation for rapid industrial growth. | Deng Xiaoping’s speeches and policy documents outlining the reform and opening-up policy. |
| 1980s-1990s | Establishment of Special Economic Zones (SEZs) | Attracted significant foreign direct investment (FDI) and spurred export-oriented manufacturing. | Data on FDI inflows into SEZs and export growth during this period. |
| 2001 | Accession to the World Trade Organization (WTO) | Further integrated China into the global trading system, accelerating its manufacturing expansion. | WTO accession agreement and subsequent trade data. |
| 2010s-Present | Focus on technological upgrading and value-added manufacturing | Shift from low-cost manufacturing to higher-tech industries and innovation-driven growth. | Government reports on industrial policy and investment in R&D. |
Key Sectors and Competitive Advantages, China is the manufacturing superpower | Hacker News
China’s manufacturing dominance spans numerous sectors, each with its own competitive advantages. These advantages are fueled by a combination of low labor costs, efficient supply chains, technological advancements, and government support.
- Electronics Manufacturing: China dominates global electronics manufacturing, leveraging its vast supply chain network and skilled workforce to produce a wide range of products, from smartphones to computers.
- Textiles and Apparel: China remains a major player in textiles and apparel, benefiting from a long history in the industry and access to raw materials.
- Automobiles: The Chinese automotive industry has experienced rapid growth, supported by government policies and increasing domestic demand.
China’s cost structure, particularly labor costs, has been a significant driver of its competitiveness. While labor costs are rising, they remain comparatively lower than in many other developed countries. The availability of a large and skilled workforce also contributes to its manufacturing prowess. Technological advancements, particularly in automation and robotics, are increasingly playing a role in maintaining China’s manufacturing edge.
Global Supply Chains and Dependence

China plays a central role in global supply chains, acting as a major producer and exporter of intermediate and final goods for various industries. Many global companies rely heavily on Chinese manufacturing for their production processes. This dependence, however, creates potential risks and vulnerabilities.
So, you’re reading about China’s manufacturing dominance on Hacker News – pretty wild, right? It makes you think about global supply chains and how things get made. This completely shifts gears, but check out this hockey news: Canucks recall Arturs Silovs, Thatcher Demko remains out vs , which is a much smaller scale but equally impactful in its own way.
Back to China, though – that manufacturing power influences everything from the hockey sticks to the jerseys.
A hypothetical scenario illustrating the consequences of a significant disruption to Chinese manufacturing could involve widespread shortages of goods, increased production costs for global companies, and disruptions to global trade. This underscores the need for diversification and resilience in global supply chains.
Challenges and Future Outlook
Despite its dominance, China’s manufacturing sector faces significant challenges. Rising labor costs, environmental concerns, and technological advancements are all factors that could impact its future leadership. Maintaining its manufacturing dominance requires a strategic shift towards higher value-added manufacturing, technological innovation, and sustainable practices.
China might face increasing competition in certain industries, particularly those requiring advanced technologies and high levels of innovation. The long-term sustainability of China’s manufacturing superpower status will depend on its ability to adapt to these challenges and embrace a more sustainable and innovation-driven model.
Illustrative Examples of Chinese Manufacturing Prowess

China’s manufacturing capabilities are evident across diverse sectors. For example, its dominance in electronics manufacturing is demonstrated by the production volumes of smartphones and other electronic devices. In textiles, China’s vast production capacity and efficient supply chains contribute to its significant global market share. The rapid growth of its automotive industry showcases its ability to compete in high-value manufacturing sectors.
So you’re reading about China’s manufacturing dominance on Hacker News? It’s a fascinating topic, especially when you consider the global impact. Take a quick break to check out the exciting highlights from the India vs Australia cricket match – India vs Australia, 5th Test, Day 2 Highlights: Rishabh Pant’s – before diving back into the complexities of China’s manufacturing superpower status.
It’s a whole different kind of power play!
Imagine a state-of-the-art Chinese manufacturing facility for electric vehicle batteries. The facility is highly automated, with robotic arms assembling battery packs with precision and efficiency. The layout is optimized for smooth material flow, minimizing waste and maximizing throughput. A highly skilled workforce operates and maintains the sophisticated machinery, ensuring high-quality production. This facility exemplifies China’s commitment to technological advancement in high-growth sectors.
The development and mass production of cost-effective lithium-ion batteries by Chinese manufacturers have significantly impacted the global electric vehicle industry, accelerating its adoption worldwide.
Closing Notes
China’s manufacturing dominance is a multifaceted phenomenon, deeply intertwined with global economics and geopolitics. While its current position is undeniable, the future holds both opportunities and challenges. Maintaining this leadership will require continuous adaptation, innovation, and addressing concerns about labor costs, environmental sustainability, and technological disruption. The story of China’s manufacturing sector is far from over; it’s a dynamic narrative that will continue to shape the global landscape for years to come.
The ongoing evolution of this sector warrants continued observation and analysis.
General Inquiries
What are some examples of Chinese manufacturing innovations that have impacted global industries?
China’s advancements in solar panel production, battery technology, and high-speed rail have significantly impacted their respective global industries, driving down costs and increasing efficiency.
How is China addressing environmental concerns within its manufacturing sector?
China is investing heavily in renewable energy sources and implementing stricter environmental regulations, although challenges remain in balancing economic growth with environmental protection.
That Hacker News thread about China’s manufacturing dominance got me thinking – a lot of those devices are probably powered by tech like Siri. If you’re one of those affected by the privacy breach, check out this payout information: Apple Siri Eavesdropping Payout—Here’s Who’s Eligible And How. It’s a reminder that even with China’s manufacturing might, data security remains a global challenge.
What are the potential risks of over-reliance on Chinese manufacturing?
Over-dependence on Chinese manufacturing creates vulnerabilities to supply chain disruptions, geopolitical instability, and potential trade conflicts.
